Seven years ago, as I was finishing my book Water is For Fighting Over, I wrote this kicker:
In the end, we need an honest reckoning with the basic problem: there is not enough water for everyone to do everything they want with it, or to use every drop to which they feel legally entitled.
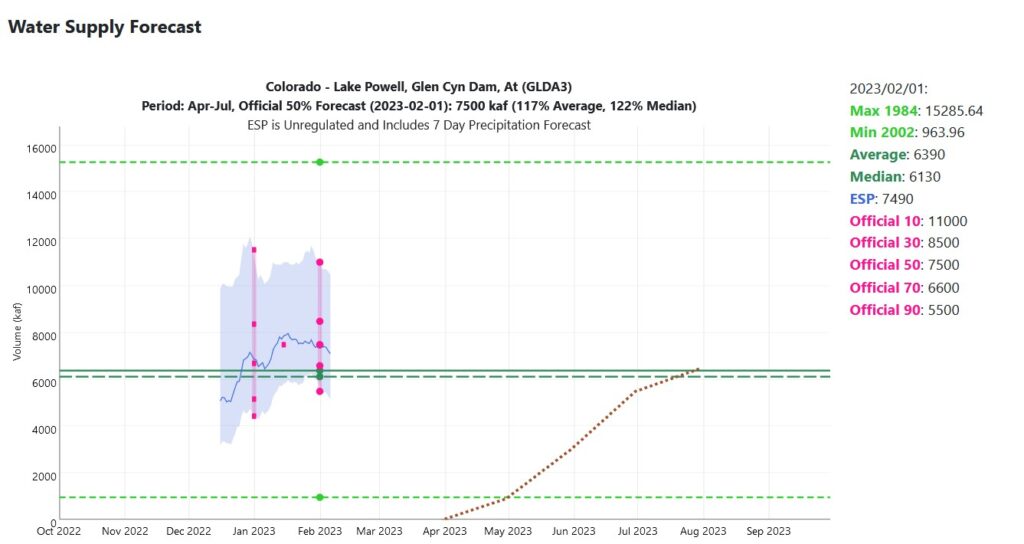
It is frequently said that the Colorado River Basin is in “crisis,” but the detailed nature of that “crisis” is rarely spelled out. It is often framed in terms of the relationship between the river’s supply and growing demand, and illustrated with pictures of the white “bathtub ring” circling the increasingly empty Lake Mead. But when demand rises above supply, and reserves in the basin’s great reservoirs run out, the basin’s water users cannot consume negative water. Someone will have to use less, or stop using altogether. Who is that? In defining the problem, then, we sooner or later have to get specific. When shortages occur, who takes the hit?
This is the point at which the river’s operating rules, and most importantly, the ambiguity about how these rules will be implemented in times of scarcity, become critical. It is also the place at which we can dimly make out the shape of long-term solutions. Without those solutions, the current rules and the physical reality of the system suggest five big risks.
The most immediate risk is Las Vegas. As we have seen, Las Vegas has demonstrated the ability to live within its means, dropping its usage over the first years of the twenty-first century so that it now consumes substantially less than its 300,000 acre-feet per year allocation. But it continues to face a physical risk. As Lake Mead drops, it becomes harder and harder for Las Vegas to get water from its intake pipes, with a clear risk that the reservoir’s level might drop so low that Las Vegas could have a legal entitlement to water that it has no physical way to get to the city.
Las Vegas is taking steps to deal with the problem, building a new intake that is deeper in the reservoir, and a new pumping plant to handle the deeper water. The first phase, the deeper pipe to take the water, opened in 2015. The completion of the pumping plant, by 2020, will eliminate the largest risk in the entire basin, which is a city of 2 million people going dry because its intake pipes are above the water line, sucking air. With a new intake deep within Lake Mead, Las Vegas’s water supply will ironically be transformed from one of the most vulnerable to one of the most secure in the Lower Basin.
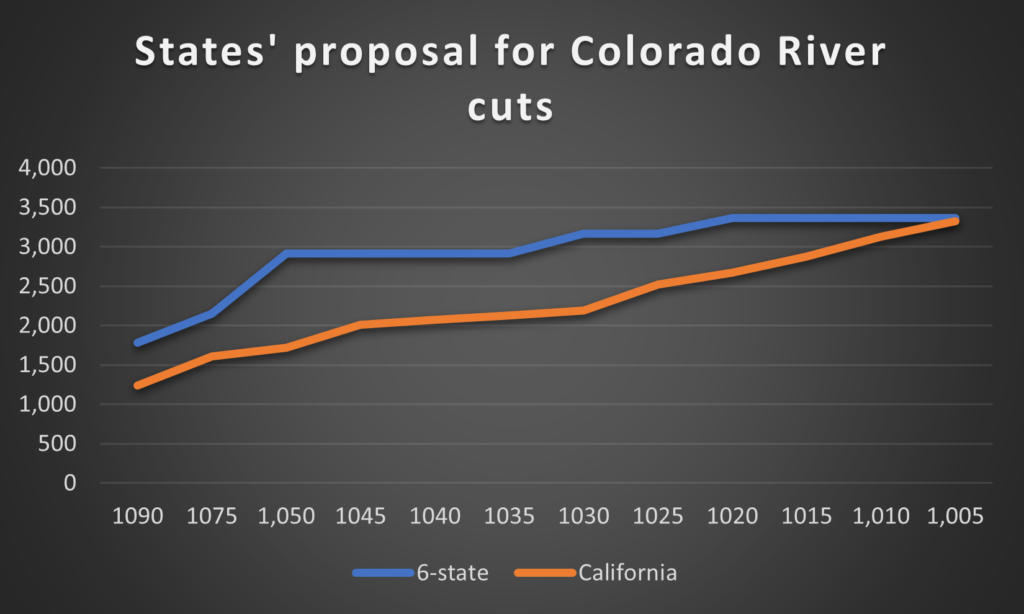
The second risk is to Arizona. As Lake Mead continues to drop, and supplies become increasingly constrained, the operating rules require that the major burden falls on Arizona. In return for the Central Arizona Project’s construction, California extracted a legal requirement (enshrined in federal law) that all of Central Arizona’s Colorado River allocation, all 1.5 million acre-feet per year that flow through the big canal to Phoenix and Tucson must be cut off completely before California loses a single drop. Arizona has long viewed subsidized agriculture as a buffer, and it has been banking surplus groundwater as a hedge against such an inevitability. This, too, will be tested.
The third risk is to the states of the Upper Colorado River Basin. Most legal scholars agree that if (when?) the total flow in the river drops because of climate change, the rules enshrined in the Colorado River Compact require the Upper Basin to continue sending 7.5 million acre-feet downstream past Lee’s Ferry each year. If climate change push
comes to shove and there is not enough water to meet that requirement and also supply all the current water use needs in Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, and New Mexico, those Upper Basin water uses must be cut to meet the Lee’s Ferry delivery requirement.The fourth risk is the long-festering problem of Native American communities’ rights to water. Unresolved, this uncertainty leaves these communities without the water they need to prosper, and it also leaves a cloud of uncertainty over other water users.
The fifth risk always remains the delta and, more broadly, the environment. The operating rules have long left environmental flows entirely out of the picture, and it is only slowly and at great pain and expense that water has been carved out to bring the environment back.
I’d say that, with only a few minor tweaks, it holds up pretty well!