A dwindling Rio Grande. Albuquerque, New Mexico, Aug. 1, 2020
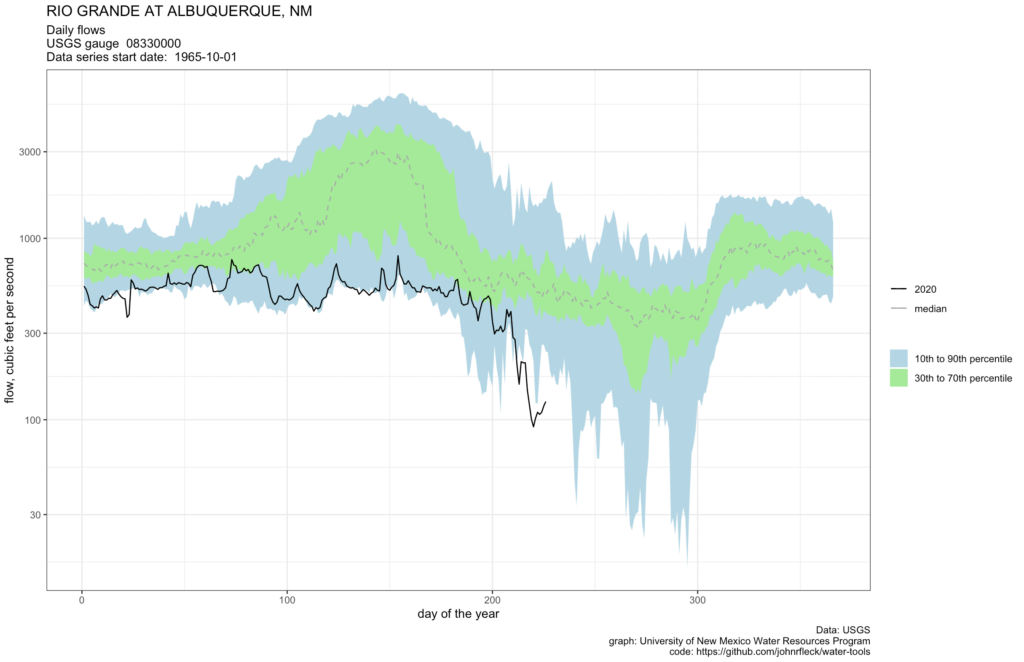
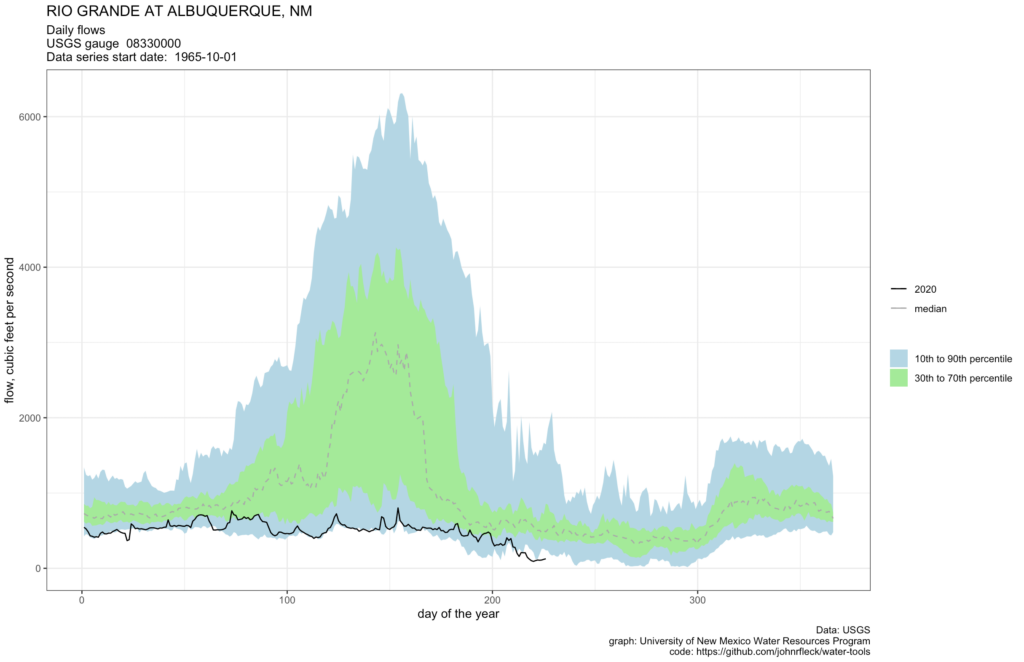
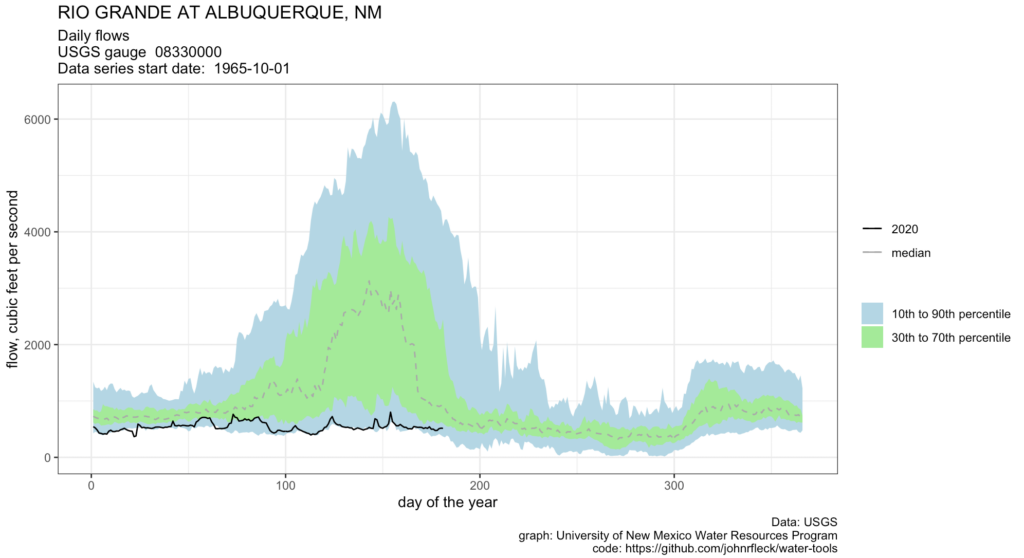
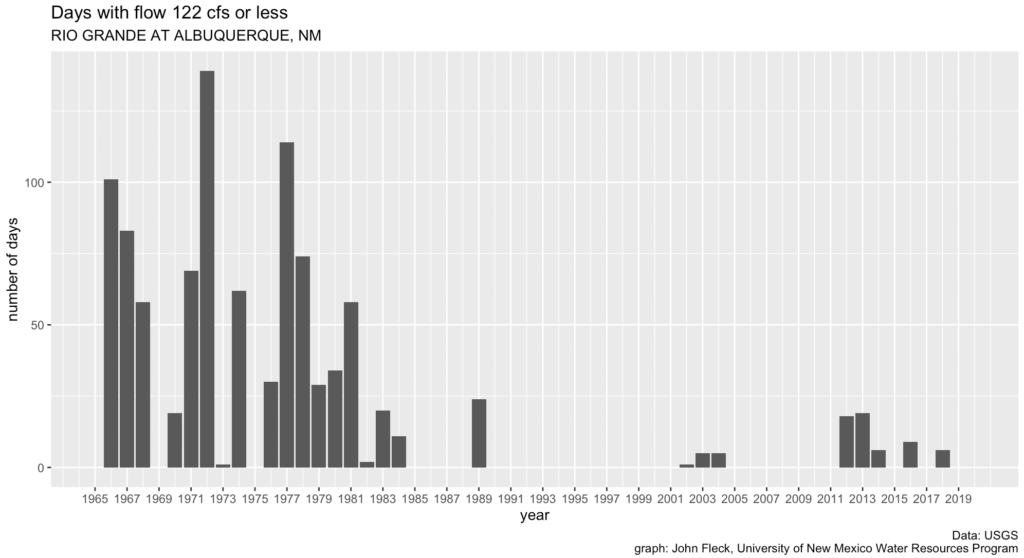
Long story short, the Rio Grande through Albuquerque has dropped to its lowest levels for this time of year since the 1980s.
The flow at the Central Avenue Bridge when I stopped to look on this morning’s bike ride was just 108 cubic feet per second. The last time it’s been that low at this point in the year appears to be 1984.
The reasons behind the low flows are a combination of hydrology and institutions. The hydrology – the water nature delivered us this year – is crappy small. The institutions, meanwhile, place primacy on the continued human use of what meager flows we do get.
To be clear, I am not making a normative statement when I say that. Those institutions reflect society’s values, and we clearly get tremendous value from that water in the alternative uses to which we put it. What I’m really interested in is thinking through and making the tradeoffs explicit.
Welcome, then, to a new semester of the University of New Mexico Water Resources Program‘s Contemporary Issues in Water Management class, which starts up in a couple of weeks. This year’s students will be joining my UNM colleague Bob Berrens and I in exploring the questions of how and why rivers go dry.
Bob and I have been busy getting ready for the strangest of fall semesters as we head into our eighth year teaching the foundational course in the University of New Mexico’s Water Resources Program. We’ll be doing it nearly entirely remotely, with readings and recorded lectures and Zoom meetings galore.
Evening walks (Bob and I are neighbors and close friends) have become a respite from the respective craziness of our university duties – I’m the director of a small graduate program, Bob (a resource economist by academic background) is chair of the Department of Economics. Figuring out how to keep our faculty and students moving in the midst of a pandemic that has effectively shut down the physical university is a great challenge. Walking and talking about what we are teaching has become our respite as we learn to speak loudly through masks across a social distance that felt awkward at first but now comes naturally.
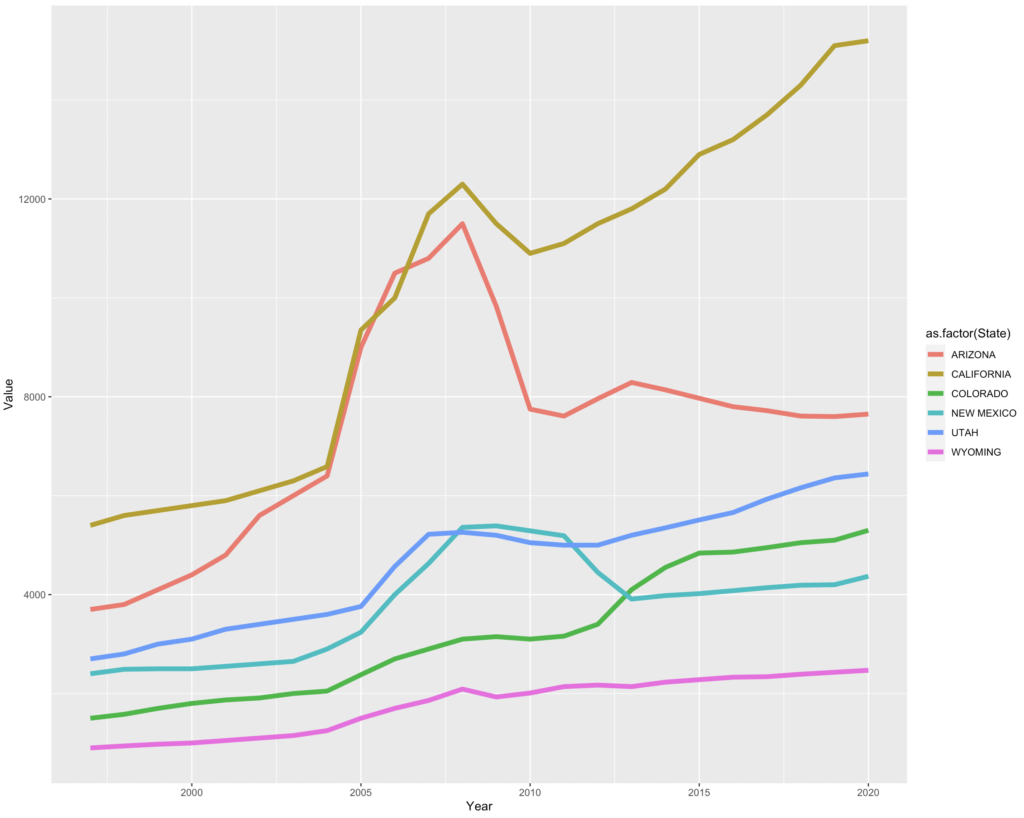
A couple of our students, Tylee Griego and Talisa Barancik, funded through the South Central Climate Adaptation Science Center, spent the summer assembling datasets on agricultural water use along the Rio Grande – in the San Luis Valley of southern Colorado, where perhaps half a million acres is irrigated, and here in the Albuquerque reach of the river, where we irrigate another 50,000 to 60,000 acres.
One of the things Bob helped me understand early on in our intellectual partnership is the importance of disaggregating agricultural water use in our policy analysis. People farm in many ways and for many different reasons, and treating it all as “ag water” misses important distinctions that have profound implications for management.
Up in the San Luis Valley, agriculture is a central pillar of the regional economy – “money farming,” I call it. Here in what we call the “middle valley”, stretching from Cochiti in the north to Elephant Butte Reservoir in the south, agriculture on net loses money. On the majority of the middle valley’s acreage, people are farming here for other reasons than cash income. Farm size seems to be a critical variable to measure this. Here in New Mexico’s Middle Rio Grande Valley, the number of farms is going up, while net cash farm income goes down. That has enormous water policy implications. Money farmers are more likely to sink deep wells and overpump aquifers, which we’re seeing in the San Luis Valley. Farmers here, farming increasingly tiny parcels with a job in town – “custom and culture” farmers, to borrow a phrase I learned from The Nature Conservancy’s Martha Cooper – are more able to simply go without.
Riding bikes to check Saturday (important field work as well as important pandemic mental health management) my friend Scot and I rode down the San Antonio Arroyo, a concrete-lined flood control channel that has been repurposed by folks in the west side neighborhood around it into a nice walking path to the river. As you can see from the picture above, what water remains in the Rio Grande has broken into braided, meandering shallows. What fish remain have become easy pickings for egrets in the shallow water.

The Albuquerque Drain, where the Barr Canal splits off to farms on Albuquerque south side, east of the Rio Grande
Downstream, meanwhile, we found the Albuquerque Drain, which parallels the Rio Grande’s eastern edge through our city’s downtown area, carrying more water than the river’s main channel. If getting water to irrigators is one’s goal, the valley’s agricultural ditch system is more efficient, with lower evaporation and other system losses, than the main river channel.
This is, in fact, an enormously clever adaptation to scarcity if our institutions and community values support human use of water. I’ve been riding my bike a lot in the Time of Pandemic on the valley ditchbanks. They are unusually dense with neighborhood walkers, and despite the impact of drought and climate change-driven aridification, the valley is green. It’s lovely.
This is the heart of the question Bob and I want our students to think through this fall – how did those institutions get to be the way they are? How might they change in the future as the community’s values change? Who is being left out as we make these decisions?
I’m not gonna lie, this pandemic is shitty in so many ways. My problems are small compared to the tragedies faced by many. It pains me to not be able to sit down with our new group of students in two weeks to begin our great adventure together. But I think Bob and I have done some good work to ready some really good questions for them to think about – questions to which we don’t know the answers.